Arduin-Row uses tinyML to improve your rowing technique
Arduin-Row uses tinyML to improve your rowing technique
Arduino Team — July 2, 2022
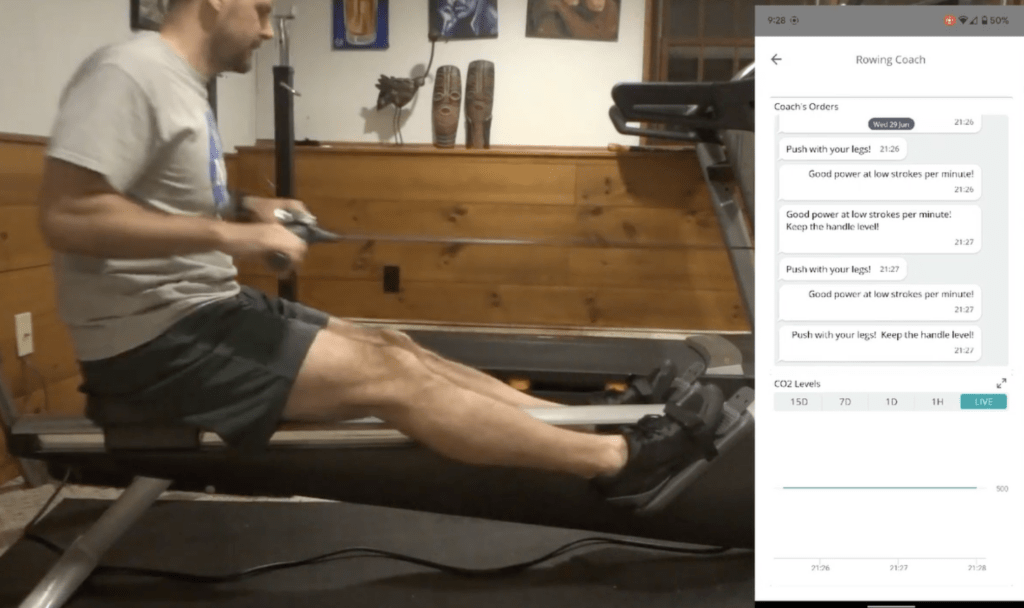
Rowers are great aerobic workouts because they involve repeatedly pushing the legs against the base and pulling the handle to achieve the fastest times. But due to the nature of the equipment, learning to train properly on one often requires a coach who can correct the form of the user, which is why Justin Lutz created the Arduin-Row.
>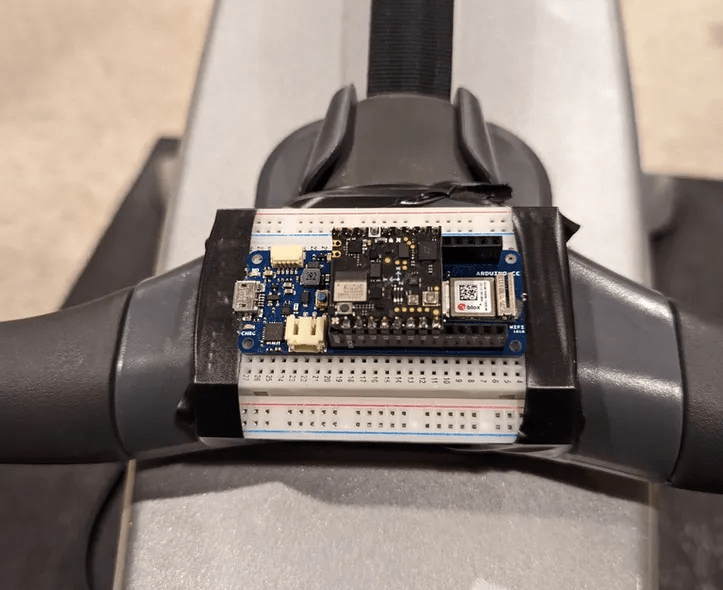
The Arduino-Row uses the accelerometer and Bluetooth® Low Energy capabilities found on the Nicla Sense ME board which was mounted as a shield on an Arduino MKR WiFi 1010. To collect data for its machine learning model , Lutz took advantage of Edge Impulse's Data Forwarding tool to capture data and send it to Edge Impulse Studio. From there, it labeled each sample as "easy", "high spm" or "low spm" and trained a Keras model that was able to successfully recognize the current motion about 98% of the time.
Lutz has expanded the project even further by incorporating the Nicla's onboard eCO2 sensor to plot an estimate of the amount of power generated by the rower. Once deployed, the code allows users to see a list of feedback given by the virtual coach and view a chart of their CO2 spent through the IoT Cloud Remote app.
You can read more about the Arduino-Row on its Edge Impulse documentation page or view the public project here in Edge Impulse Studio.
Arduino Team — July 2, 2022

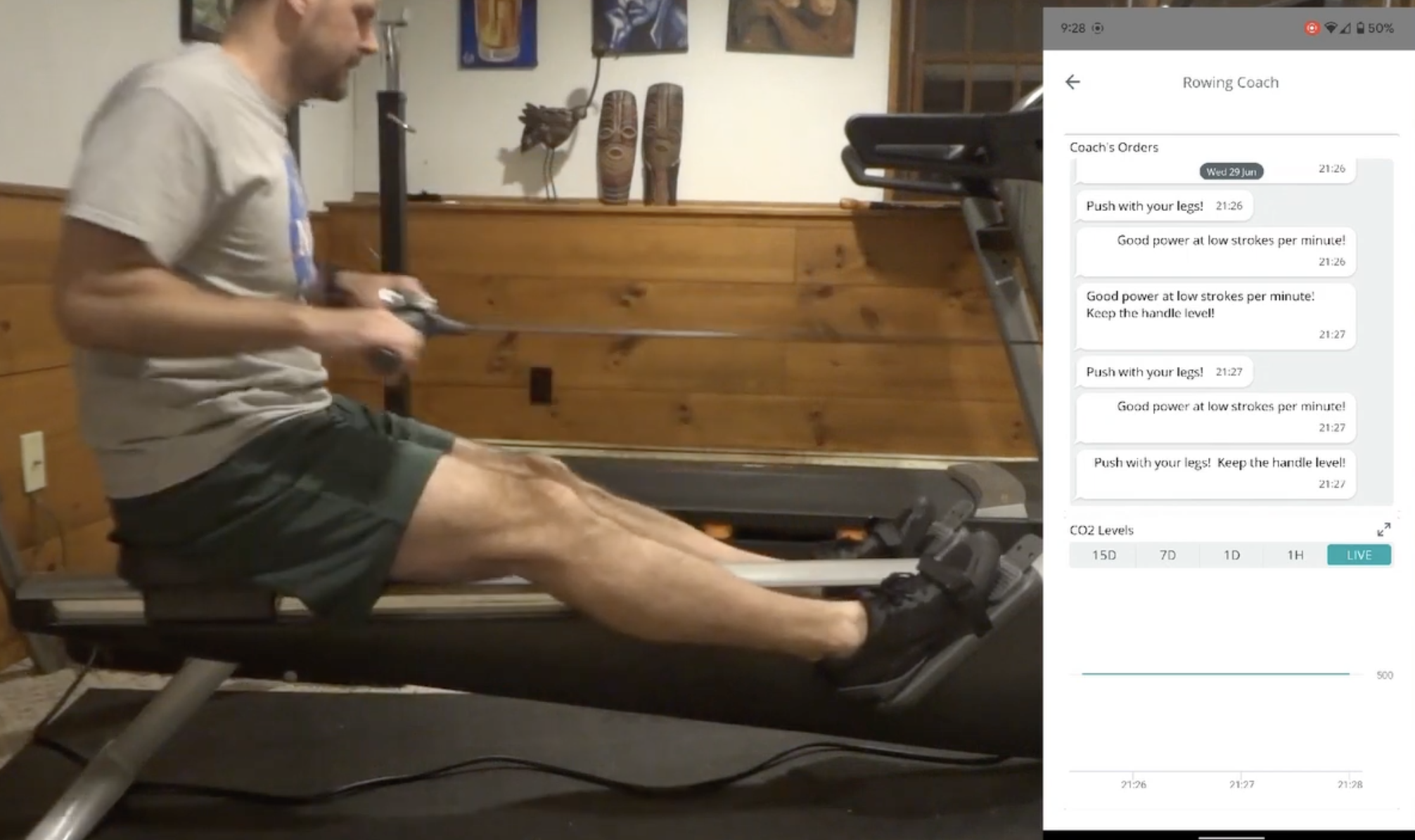
Rowers are great aerobic workouts because they involve repeatedly pushing the legs against the base and pulling the handle to achieve the fastest times. But due to the nature of the equipment, learning to train properly on one often requires a coach who can correct the form of the user, which is why Justin Lutz created the Arduin-Row.
>
The Arduino-Row uses the accelerometer and Bluetooth® Low Energy capabilities found on the Nicla Sense ME board which was mounted as a shield on an Arduino MKR WiFi 1010. To collect data for its machine learning model , Lutz took advantage of Edge Impulse's Data Forwarding tool to capture data and send it to Edge Impulse Studio. From there, it labeled each sample as "easy", "high spm" or "low spm" and trained a Keras model that was able to successfully recognize the current motion about 98% of the time.
Lutz has expanded the project even further by incorporating the Nicla's onboard eCO2 sensor to plot an estimate of the amount of power generated by the rower. Once deployed, the code allows users to see a list of feedback given by the virtual coach and view a chart of their CO2 spent through the IoT Cloud Remote app.
You can read more about the Arduino-Row on its Edge Impulse documentation page or view the public project here in Edge Impulse Studio.
What's Your Reaction?






















