Pecking Order Theory: How to Order Funding Sources
The pecking order theory or pecking order model explains how firms prioritize funding sources for an optimal choice of capital structure, while balancing long-term debt and equity financing.
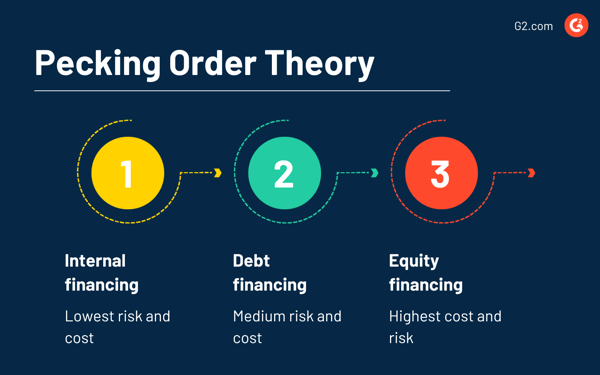
Managers who follow this corporate finance model follow a hierarchy while investing in opportunities. They favor using internal funds or retained earnings before exploring other options. Debt is the next option once they run out of internal funding.
Equity financing is their last resort when debt no longer seems viable.
What is pecking order theory?The pecking order theory of capital structure states that business leaders prioritize corporate financing transactions based on a hierarchy in which they use retained earnings first (internal financing) , then debt financing and finally equity financing.
Financial analysis software and financial risk management software play an important role in how companies analyze their cash flow and financial economics to find sources of funding. Myers and Majluf popularized pecking order theory to help companies make sound financing decisions.
Pecking Order Theory and Capital Structure ExplainedInternal funding is the first choice in pecking order theory because there is no additional cost associated with its use. Companies that use retained earnings for financing do not have to pay borrowing or equity costs.
Debt financing comes second because of the interest payments associated with the use of borrowed capital. Whether the company takes out commercial loans or issues corporate bonds, it will have to pay interest, which will make the cost of debt higher than the nonexistent cost of using retained earnings.
Equity financing comes last in the pecking order theory because it affects profitability and is the most expensive option. The cost of equity (e.g. stock) is higher than the cost of debt financing.
Investors often view a stock issue as a telltale sign of a stock valuation above market value. They treat this signal as an indicator that stock prices will soon fall.
This misunderstanding is due to information asymmetry, the central idea of pecking order theory. Asymmetric information or information failure occurs when one party or individual has more information than the other party or individual.
Executives know more about company performance, prospects, future prospects, or risks than creditors, investors, creditors, or shareholders. Because of this knowledge imbalance, external users demand a higher cost of capital to offset the risk. When companies issue stock to fund themselves, they end up paying more because of this information asymmetry.
The ultimate goal is to use the theory of trade-offs to optimize the capital structure of the company, which creates the right balance between debt, equity and other determinants.
Example of pecking order theoryImagine you're a business owner deciding how to fund an exciting new project. You have calculated the costs and you will need $15,000 to put this idea into action. You have three options.
Option 1: If you have $15,000 of retained earnings, you can...
The pecking order theory or pecking order model explains how firms prioritize funding sources for an optimal choice of capital structure, while balancing long-term debt and equity financing.
Managers who follow this corporate finance model follow a hierarchy while investing in opportunities. They favor using internal funds or retained earnings before exploring other options. Debt is the next option once they run out of internal funding.
Equity financing is their last resort when debt no longer seems viable.
What is pecking order theory?The pecking order theory of capital structure states that business leaders prioritize corporate financing transactions based on a hierarchy in which they use retained earnings first (internal financing) , then debt financing and finally equity financing.
Financial analysis software and financial risk management software play an important role in how companies analyze their cash flow and financial economics to find sources of funding. Myers and Majluf popularized pecking order theory to help companies make sound financing decisions.
Pecking Order Theory and Capital Structure ExplainedInternal funding is the first choice in pecking order theory because there is no additional cost associated with its use. Companies that use retained earnings for financing do not have to pay borrowing or equity costs.
Debt financing comes second because of the interest payments associated with the use of borrowed capital. Whether the company takes out commercial loans or issues corporate bonds, it will have to pay interest, which will make the cost of debt higher than the nonexistent cost of using retained earnings.
Equity financing comes last in the pecking order theory because it affects profitability and is the most expensive option. The cost of equity (e.g. stock) is higher than the cost of debt financing.

Investors often view a stock issue as a telltale sign of a stock valuation above market value. They treat this signal as an indicator that stock prices will soon fall.
This misunderstanding is due to information asymmetry, the central idea of pecking order theory. Asymmetric information or information failure occurs when one party or individual has more information than the other party or individual.
Executives know more about company performance, prospects, future prospects, or risks than creditors, investors, creditors, or shareholders. Because of this knowledge imbalance, external users demand a higher cost of capital to offset the risk. When companies issue stock to fund themselves, they end up paying more because of this information asymmetry.
The ultimate goal is to use the theory of trade-offs to optimize the capital structure of the company, which creates the right balance between debt, equity and other determinants.
Example of pecking order theoryImagine you're a business owner deciding how to fund an exciting new project. You have calculated the costs and you will need $15,000 to put this idea into action. You have three options.
Option 1: If you have $15,000 of retained earnings, you can...
What's Your Reaction?






















