Detect vandalism using audio classification on the Nano 33 BLE Sense
Detect vandalism using audio classification on the Nano 33 BLE Sense
Arduino Team — December 1, 2022

Bringing in and/or destroying something is an act that most people hope to avoid completely or at least catch the perpetrator when it happens. And as Nekhil R. notes in his project description, traditional deterrence/detection methods often fail, meaning a new kind of solution was needed.
Unlike other glass break sensors, Nekhil's project relies on a single inexpensive Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense and its built-in digital microphone to record audio, classify it, and then alert a homeowner via WiFi via an ESP8266-01 card. The dataset used to train the machine learning model came from two sources: the Microsoft Scalable Noisy Speech dataset for background noise and broken glass recorded on the device itself. Both of these were added to an Edge Impulse project through the Studio and split into two-second samples before being processed by a Mel-filterbank Energy (MFE) algorithm.
 100
100
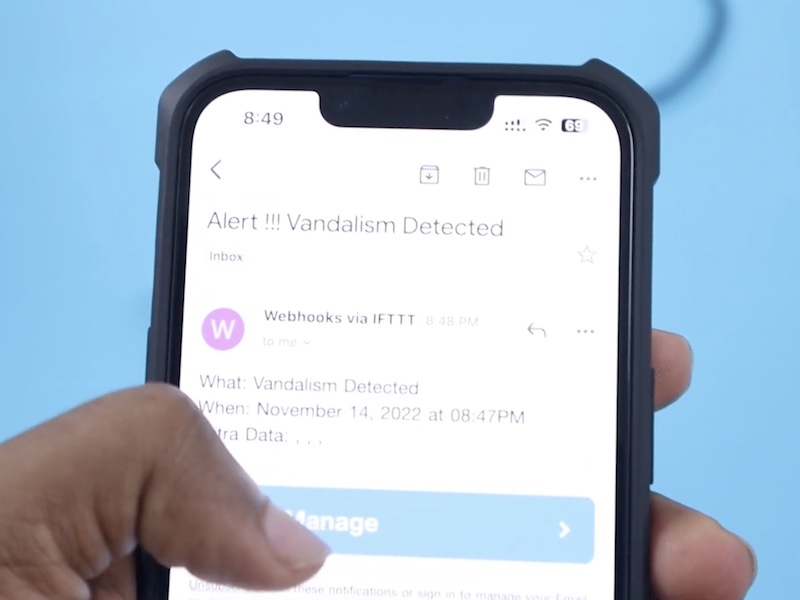
The resulting model, trained using 200 training cycles and slight noise additions, yielded an impressive 92% accuracy, with some glass breakage samples being misclassified as a mere noise. This was then exported to the Nano 33 BLE Sense as a library for use in a sketch that continuously classifies incoming sounds and sends an email using IFTTT if glass breakage is detected.
You can watch Nekhil's demo video below and read more about this project here on the Edge Impulse blog.
Arduino Team — December 1, 2022

Bringing in and/or destroying something is an act that most people hope to avoid completely or at least catch the perpetrator when it happens. And as Nekhil R. notes in his project description, traditional deterrence/detection methods often fail, meaning a new kind of solution was needed.
Unlike other glass break sensors, Nekhil's project relies on a single inexpensive Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense and its built-in digital microphone to record audio, classify it, and then alert a homeowner via WiFi via an ESP8266-01 card. The dataset used to train the machine learning model came from two sources: the Microsoft Scalable Noisy Speech dataset for background noise and broken glass recorded on the device itself. Both of these were added to an Edge Impulse project through the Studio and split into two-second samples before being processed by a Mel-filterbank Energy (MFE) algorithm.
 100
100
The resulting model, trained using 200 training cycles and slight noise additions, yielded an impressive 92% accuracy, with some glass breakage samples being misclassified as a mere noise. This was then exported to the Nano 33 BLE Sense as a library for use in a sketch that continuously classifies incoming sounds and sends an email using IFTTT if glass breakage is detected.
You can watch Nekhil's demo video below and read more about this project here on the Edge Impulse blog.
What's Your Reaction?















![Three of ID's top PR executives quit ad firm Powerhouse [EXCLUSIVE]](https://variety.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/ID-PR-Logo.jpg?#)







