solar energy in motion
Tell me the steps
It's fun to use mini solar cells to charge your gear or power small gadgets, and once you've learned the basics, you can upgrade to larger panels. Let's explore how you can harness solar power for your own DIY projects - mobile, portable or otherwise - and say goodbye to (some) batteries and plugging things in!
Early solar powerWhile the first solar electric panel is attributed to Bell Laboratories in 1954, a variety of other solar powered devices have been around for hundreds of years. The cell produced by Bell chemist Calvin Fuller and physicists Daryl Chapin and Gerald Pearson was the first silicon solar cell, following their success with semiconductors in 1947.
Solar thermal energy has also been used in a variety of ways, including by architect Eleanor Raymond and MIT engineer Maria Telkes for the Dover Sun House in 1948 (Figure A

Of course, solar energy dates back to ancient civilizations using the sun to dehydrate food, using magnifying glasses to light fires, using reflection and positioning to tell the time or light up a room, among other uses. . When you think about it like this, contemporary solar cells are just one point on a long continuum of solar possibilities!
Photovoltaic phenomenaSolar panels use what we call the photovoltaic effect, the ability of a material to emit electrons when exposed to light, to generate electricity. This effect was observed as early as 1839 by the French physicist Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel, who discovered that metal electrodes in an electrolyte solution produced a current when exposed to solar radiation. Although he couldn't explain it at the time, it laid the groundwork for what was to come.
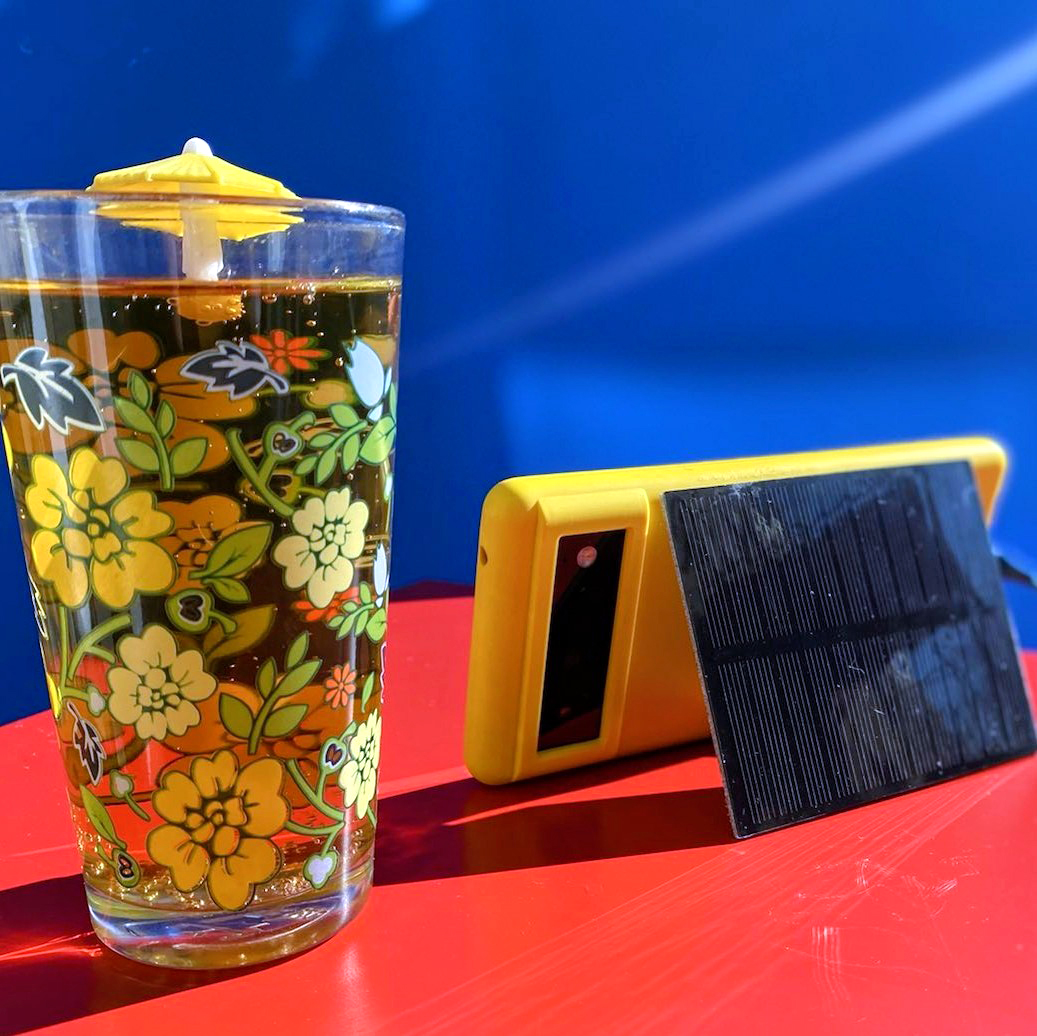

Tell me the steps
It's fun to use mini solar cells to charge your gear or power small gadgets, and once you've learned the basics, you can upgrade to larger panels. Let's explore how you can harness solar power for your own DIY projects - mobile, portable or otherwise - and say goodbye to (some) batteries and plugging things in!
Early solar powerWhile the first solar electric panel is attributed to Bell Laboratories in 1954, a variety of other solar powered devices have been around for hundreds of years. The cell produced by Bell chemist Calvin Fuller and physicists Daryl Chapin and Gerald Pearson was the first silicon solar cell, following their success with semiconductors in 1947.
Solar thermal energy has also been used in a variety of ways, including by architect Eleanor Raymond and MIT engineer Maria Telkes for the Dover Sun House in 1948 (Figure A

Of course, solar energy dates back to ancient civilizations using the sun to dehydrate food, using magnifying glasses to light fires, using reflection and positioning to tell the time or light up a room, among other uses. . When you think about it like this, contemporary solar cells are just one point on a long continuum of solar possibilities!
Photovoltaic phenomenaSolar panels use what we call the photovoltaic effect, the ability of a material to emit electrons when exposed to light, to generate electricity. This effect was observed as early as 1839 by the French physicist Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel, who discovered that metal electrodes in an electrolyte solution produced a current when exposed to solar radiation. Although he couldn't explain it at the time, it laid the groundwork for what was to come.
What's Your Reaction?














![Three of ID's top PR executives quit ad firm Powerhouse [EXCLUSIVE]](https://variety.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/ID-PR-Logo.jpg?#)







